js手撕笔记
手写 instanceof
检查 B 是否为 A 的父类或者祖先类型的函数,原理是利用 js 对象原型链和原型对象的知识一层一层寻找,最底层是 null:
let myInstanceof = (target,origin) => {
while(target) {
if(target._proto_===origin.prototype) {
return true;
}
target=target._proto_;
}
return false;
}
// 测试
let a = [1,2,3];
console.log(myInstanceof(a,Array)); // true
console.log(myInstanceof(a,String)); // false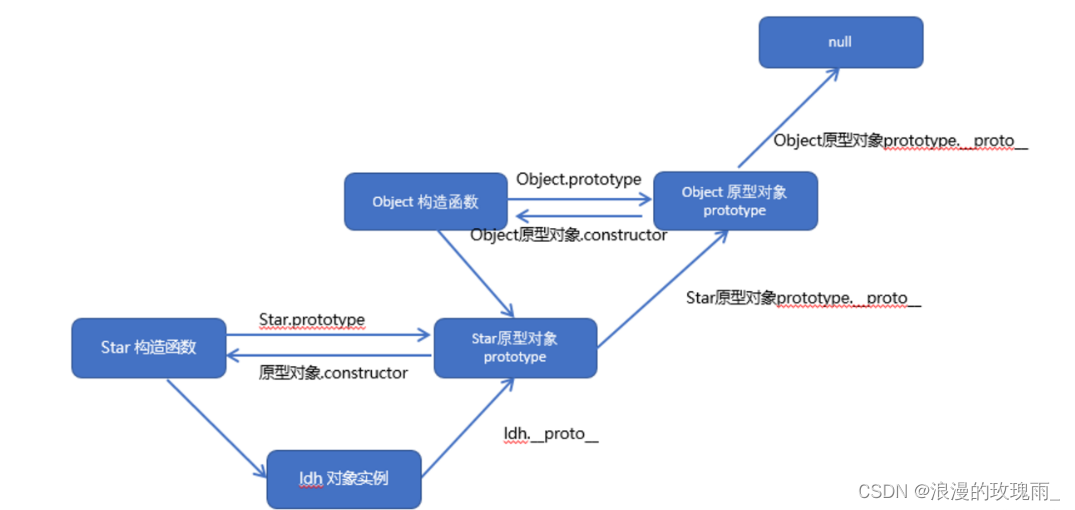 每个函数对象都有自己的 prototype,如果直接
每个函数对象都有自己的 prototype,如果直接 a.prototype 返回的是 undefined,但是 Object.prototype 和 Array.prototype 等则有具体的属性值,因为这些函数对象有完整的原型链。对象通过 __proto__ 来访问上一层的 prototype。
例如 a.__proto__ === Array.prototype
原生实现数组 map 方法
Map 参数:
- callback 函数
- currentValue 当前元素
- index(可选)当前元素下标
- array(可选)调用 map() 的数组
- thisArg 修改执行 map 时的 this 指向
Array.prototype.myMap = function(callback) {
let res=[];
for(let i=0;i<this.length;i++) {
res.push(callback(this[i],i,this));
}
return res;
}
// use
let a=[1,2,3];
let b=a.myMap((item)=>item+1);
console.log(b); // [2,3,4]原生实现数组 reduce 方法
Reduce 参数:
- callback 函数
- previousValue 上一次调用的返回值或者初始值
- currentValue 当前元素
- currentIndex 当前元素下标
- array 调用 reduce () 的数组
- initialValue (可选)初始值,作为第一次调用 callback 时传给 previousValue 的值
Array.prototype.myReduce = function(callback, initialValue) {
let num=initialValue==undefined?this[0]:initialValue;
for(int i=initialValue==undefined?0:1;i<this.length;i++) {
num=callback(num,this[i],i,this);
}
return num;
}
// use
let a=[1,2,3];
let res=a.myReduce((acc,item)=>acc+item,0); // 累加使用 reduce 实现 map 方法
Array.prototype.myMap = function(callback) {
return this.reduce((acc,item)=>{ // reduce函数最后返回累加器即acc
acc.push(callback(item))
return acc;
},[])
}
// use
let a=[1,2,3];
let b=a.myMap((item)=>item+1);
console.log(b); // [2,3,4]使用 reduce 实现数组扁平化
数组扁平化意为将多维数组压缩成一维数组,concat 方法主要用于合并~
let flatten = function(arr) {
return arr.reduce((acc,item)=>{
return acc.concat(Array.isArray(item) ? flatten(item) : item);
},[])
}
// use
let a=[1,2,[3,4]];
flatten(a);
console.log(a); // [1,2,3,4]实现柯里化函数
柯里化是指将一个多参数的函数转换成一系列单参数函数,实参个数>=形参个数时会执行该函数,多于参数忽略,如果小于则需要再接收实参,如果中止会返回 NaN
let curry = function(fn, ...arg) {
return fn.length<=arg.length?fn(...arg):curry.bind(null,fn,...arg);
// fn.length返回形参即fn需要的参数,使用bind目的是返回一个函数,其他(call apply)会返回值,不适用
}
// use
function sum(a,b,c) {
return a+b+c;
}
let sumCurry=curry(sum);
console.log(sumCurry(1,2,3)); // curry(sum)(1,2,3) = 6
console.log(sumCurry(1,2)(3)); // 6
console.log(sumCurry(1,2,3,4)); // 6
console.log(sumCurry(1,2)); // NaN浅拷贝及深拷贝
修改原对象的嵌套对象属性值时,深拷贝得到的对象不会受到影响,而浅拷贝得到的会
const shallowcopy=function(obj) {
const newObj={};
for(const key in obj) {
newObj[key]=obj[key];
}
return newObj;
}
const deepcopy=function(obj) {
const newObj={};
for(const key in obj) {
if(typeof obj[key]==='object') {
newObj[key]=deepcopy(obj[key]);
}else {
newObj[key]=obj[key];
}
}
return newObj;
}
// use
const a={a:1,b:{c:2}};
const b=shallowcopy(a);
const c=deepcopy(a);
a.b.c=3;
console.log(b.b.c); // 3
console.log(c.b.c); // 2手写 call apply bind
这三个主要起到一个调用时改变 this 指向的作用 call:
Function.prototype.myCall=function(context,...args) {
context=context||window;
const fn=Symbol();
context[fn]=this; // 即foo
const result=context[fn](...args); // 即foo(...args)
delete context[fn];
return result;
}apply:
和 call 的不同是,它传入的是一个数组,而 call 传入的是一个个单独的参数。
代码除了接收的是 args 而不是 ...args 以外,和 call 一模一样,因为 ...args 也可以指展开数组 args
Function.prototype.myApply=function(context, args) {
context=context||window;
const fn=Symbol();
context[fn]=this;
const result=context[fn](...args);
delete context[fn];
return result;
}bind:
和前两个不同的是他会返回一个新的函数等待被调用,而不是直接返回一个值,接收的参数是独立的,不同于 apply 的数组,所以要用 concat 进行合并此时是一个数组,所以用 myApply
Function.prototype.myBind=function(context,...args) {
context=context||window;
const fn=this; // 即foo
return function(...newArgs) {
return fn.myApply(context,args.concat(newArgs));
}
}
// use
let obj={name:"Amy"};
function foo(a,b,c) {
console.log(this.name, a+b+c);
}
foo.myCall(obj,1,2,3); // Amy 6
foo.myApply(obj,[1,2,3]); // Amy 6
foo.myBind(obj,1,2)(3); // Amy 6睡眠函数
// 请你编写一个异步函数,它接收一个正整数参数 millis ,并休眠 millis 毫秒。要求此函数可以解析任何值。
/**
* @param {number} millis
* @return {Promise}
*/
async function sleep(millis) {
return new Promise(resolve=>setTimeout(resolve, millis))
}
let t = Date.now()
sleep(100).then(() => console.log(Date.now() - t)) // 100手动实现 new
/**
* function Person(name, age) {
* this.name=name
* this.age=age
* }
* let p=myNew(Person,'Tom',17)
* console.log(p)
*/
function myNew() {
let obj={}
let Constructor=[].shift.call(arguments)
obj.__proto__=Constructor.prototype
let res=Constructor.apply(obj,arguments)
return typeof res==='object'?res:obj
}
手写 Promise
Promise 最主要有三个状态:加载中 pending、兑现 fulfilled、拒绝 rejected,根据状态的不同做出不同的处理
const Status = {
PENDING:'pending',
FULFILLED:'fulfilled',
REJECTED:'rejected'
}
class myPromise {
Constructor(executor) {
this.status=Status.PENDING
this.value=undefined
this.reason=undefined
this.onFulfilledQueue=[]
this.onRejectedQueue=[]
const resolve = value => {
if(this.status===Status.PENDING) {
this.status=Status.FULFILLED
this.value=value
this.onFulfilledQueue.forEach(fn=>fn())
}
}
const reject = reason => {
if(this.status===Status.PENDING) {
this.status=Status.REJECTED
this.reason=reason
this.onRejectedQueue.forEach(fn=>fn())
}
}
executor(resolve,reject)
}
}手写 then 和 all 方法,then 属于每个实例都用到的、all 属于所有实例都可用的,对标的对象不同所以 then 要用 MyPromise.prototype.then=... 写,all 要用 MyPromise.all=... 写~
MyPromise.prototype.then=function(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if(this.status===Status.FULFLILLED) onFulfilled(this.value)
if(this.status===Status.REJECTED) onRejected(this.reason)
if(this.status===Status.PENDING) {
this.onFulfilledQueue.push(()=>onFulfilled(this.value))
this.onRejectedQueue.push(()=>onRejected(this.reason))
}
}
MyPromise.all=function(promises) {
return new MyPromise((resolve,reject)=>{
let res=[] // 存结果
let count=0
promises.forEach((promise,index)=>{ // 同时执行多个异步
promise.then(value=>{
res[index]=value
count++
if(count===promises.length) {
resolve(res)
}
},reject) // 有任意一个拒绝了就直接返回拒绝
})
})
}
// 和all不同的是race方法中只要有一个成功或失败了就直接返回
MyPromise.race=function(promises) {
return new MyPromise((resolve,reject)=>{
promises.forEach(promise=>{ // 同时执行多个异步
promise.then(resolve,reject)
})
})
}解析 url 字符串里的参数
基础 map 版
function parse(url) {
let obj={}
url
.slice(url.indexOf('?')+1)
.split('##')[0]
.split('&')
.map(item=>{
const[key,value]=item.split('=')
obj[key]=value
})
return obj
}基础 reduce 版
function parse(url) {
return url
.split('?')[1].split('##')[0].split('&')
.reduce((acc,item)=>{
const[key,value]=item.split('=')
acc[key]=value
return acc
},{}) // 注意reduce函数必须要返回和设置初始值!!
}如果为空就不显示该参数而不是录入 undefined
function parse(url) {
return url
.split('?')[1].split('##')[0].split('&')
.reduce((acc,item)=>{
const[key,value]=item.split('=')
if(!value) return acc
acc[key]=value
return acc
},{})
}解决参数有嵌套对象或者数组的问题
function parse(url) {
return url
.split("?")[1].split("##")[0].split("&")
.reduce((acc,item)=>{
const[key,value]=item.split("=")
if(!value) return acc
const path=key.replace("[","]").split("]").fliter(x=>x)
// 把a[name]搓成[a,name]变成路径一个个找
deep_parse(acc,path,value) // 递归
return acc
},{})
}
function deep_parse(obj,path,value) {
let i=0
while(i<path.length-1) { // 最后一个值是value
if(!obj[path[i]]) {
if(path[i+1].watch(/^\d+$/)) // 匹配数字
obj[path[i]]=[]
else obj[path[i]]={}
}
obj=obj[path[i]]
i++;
}
obj[path[i]]=value;
}防抖和节流
- 节流:连续触发事件但是 n 秒内只执行一次函数,
- 防抖:触发事件后过了 n 秒才会执行,但 n 秒内如果再次触发就会重新计时,例如搜索框输入完文字以后再展示搜索联想
// 我是节流
function throttle(fn,t) {
let last=0
return function(...args) {
let nowTime=Date.now()
if(nowTime-last>=t) {
fn(...args)
last=nowTime
}
}
}
// 我是防抖
function debounce(fn,t) {
let timer=null
return function(...args) {
clearTimeout(timer)
timer=setTimeout(()=>{
fn(...args)
},t)
}
}数组去重
var arr=[2,0,2,4,1,0,0,8]
// ES6 set方法
var a_arr=[...new Set(arr)]
// indexOf方法
var a_arr=[]
for(let i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
if(a_arr.indexOf(arr[i])==-1) {
a_arr.push(arr[i])
}
}
// filter+indexOf
function unique(array) {
var res=array.filter(function(item,index,array)) {
return array.indexOf(item)===index
})
return res
}
var a_arr=unique(arr)
// for循环(懒得写了)